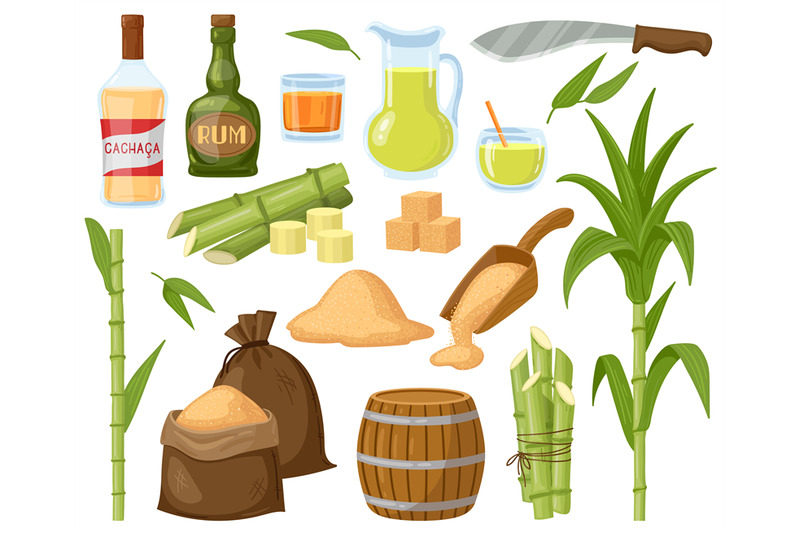
Revealing the Manufacturing Secrets Behind Sugar Cane and Its Diverse Variety Of Products
The manufacturing journey of sugar cane is intricate and multi-faceted. It starts in the fields, where mindful harvesting strategies established the stage for perfect sugar extraction. The procedure involves several phases, including juice removal and refining - sugar cane products. However, sugar cane's prospective expands much past simple sweet taste. Developments in handling and sustainable methods are improving its role in modern-day markets. What exists in advance for this flexible crop? The responses might surprise those thinking about its future
The Trip of Sugar Cane: From Field to Factory

As sugar cane persuades gently in the tropical breeze, it begins a transformative trip from field to factory. The dynamic environment-friendly stalks, rich in sucrose, are cultivated under excellent conditions, taking advantage of ample sunshine and rains. Farmers meticulously keep an eye on the development, making certain the plants reach their peak maturity, which is essential for taking full advantage of sugar content.Once grew, the cane is prepared for harvesting, where its fibrous structure holds the assurance of pleasant items. The journey continues as the stalks are delivered to processing centers, where they undergo a collection of meticulous steps. At the manufacturing facility, the cane is cleaned, shredded, and pushed to remove the juice. This juice is after that made clear and vaporized, leading the means for formation. Each stage of this journey is important, as it eventually identifies the high quality of the sugar and various other products derived from this versatile plant.
Collecting Methods: The Very First Step in Production
Harvesting sugar cane calls for accuracy and ability, as the timing and method directly influence the top quality of the final product. The procedure commonly starts with figuring out the excellent harvest, which is important; sugar content comes to a head prior to the plant gets to complete maturity. Cultivators often count on experience and farming indicators to make a decision when to harvest.Two primary techniques dominate the gathering landscape: guidebook and mechanical approaches. Hands-on harvesting, though labor-intensive, enables for mindful selection of stalks and minimizes damage. Employees utilize machetes to reduce the cane near to the base, ensuring the stalks remain undamaged for processing.Mechanical harvesting, on the other hand, utilizes specific equipment to cut and collect the cane rapidly. While this method considerably boosts efficiency, it might bring about higher degrees of debris and lower sugar content. Eventually, the picked method affects not only the amount yet also the top quality of sugar cane delivered to refining centers.
The Extraction Process: Opening the Sweet taste
The extraction process is essential for changing harvested sugar cane right into pleasant juice. Various methods of juice removal can greatly influence the top quality and yield of the end product. Recognizing these techniques is essential for maximizing the advantages of sugar cane manufacturing.
Collecting Techniques Described
Releasing the sweetness of sugar cane starts with accurate harvesting methods that assure optimal yield and quality. The procedure typically involves cutting the cane at ground degree, making sure very little damage to the plant and permitting regrowth. Farmers usually utilize machetes or specialized devices, depending upon the range of the operation. Timing is crucial; harvesting happens when the sugar web content reaches its top, usually during completely dry seasons. Additionally, employees must be trained to identify the very best stalks, avoiding those that are also old or unhealthy. Effective transportation to processing centers is additionally crucial, as hold-ups can cause sugar deterioration (sugar cane products). These careful strategies eventually lay the structure for producing premium sugar and its diverse byproducts
Juice Removal Techniques
Juice extraction is an essential action in changing sugar cane into its wonderful essence. This process commonly entails a number of methods, each designed to efficiently draw out the sugary liquid from the coarse stalks. The most usual method is milling, where the sugar cane is smashed between hefty rollers to launch the juice. One more method is diffusion, which uses warm water to dissolve the sugar from the cane fibers, making it a more efficient alternative for massive operations. In addition, some manufacturers utilize screw presses, which use mechanical pressure to remove juice. After extraction, the juice undertakes clarification to get rid of pollutants before additional processing. Each approach reflects the sector's concentrate on making best use of yield and ensuring high-grade sugar production.
Refining Sugar: Changing Raw Cane Into Granulated Gold
The refining process is essential for converting raw cane sugar right into the pure, granulated item customers acknowledge. sugar cane products. This includes a collection of removal and filtering actions to eliminate contaminations, followed by formation and drying methods that enhance the sugar's top quality. Comprehending these approaches exposes the elaborate improvement from cane to the gold granules that sweeten countless foods and beverages
Removal and Filtration Process
A crucial phase in the sugar manufacturing trip involves the extraction and purification of juice from newly collected sugar cane. This procedure starts with squashing the cane to release its wonderful juice, commonly making use of large rollers or mills. The drawn out juice has not only sugar however additionally impurities, including fibers and mud. To guarantee the juice is appropriate for additional refining, it undertakes a filtration process. This involves passing the juice through various filters and clarifiers to remove solid particles and undesirable products. Chemicals such as lime might be included in assist in the explanation procedure. The outcome is a clear, raw cane juice that offers as the foundation for creating refined sugar, Going Here ready for subsequent phases of handling.
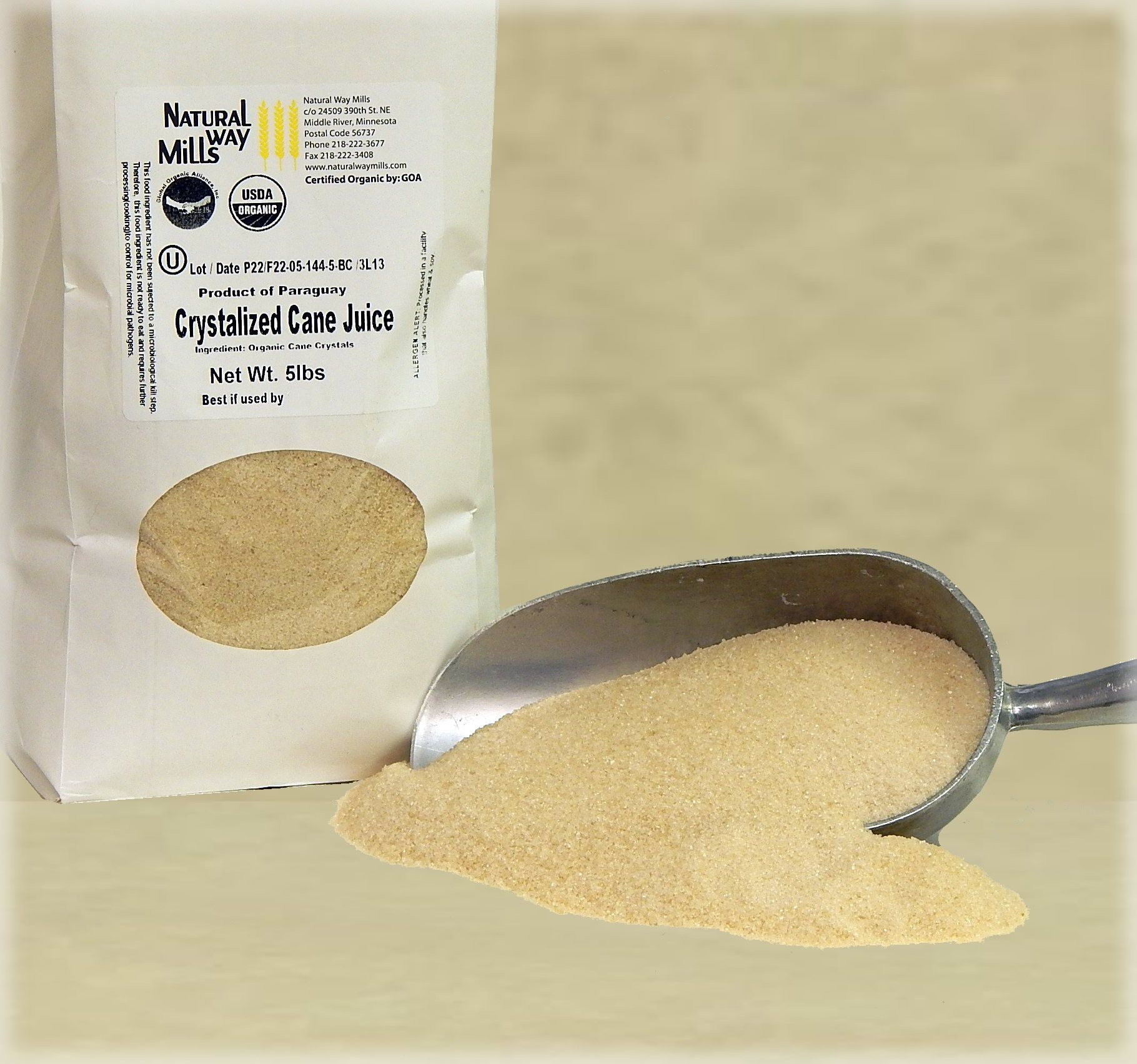

Crystallization and Drying Out Methods
After the extraction and filtration processes produce clear raw cane juice, the next action in sugar production is crystallization. This procedure involves steaming the juice to evaporate water, enabling sugar molecules to create crystals. As the liquid thickens, it gets to supersaturation, prompting sugar to take shape. The blend is after that cooled, advertising additional crystal development. Once formation is complete, the sugar crystals are divided from the staying syrup with centrifugation.The last stage involves drying out, where the crystals are revealed to warm air to remove recurring moisture. This step is necessary, as it guarantees the product accomplishes the desired granulation and rack stability. The outcome is pure, granulated sugar, prepared for packaging and distribution.
Beyond Sweet Taste: Diverse Products From Sugar Cane
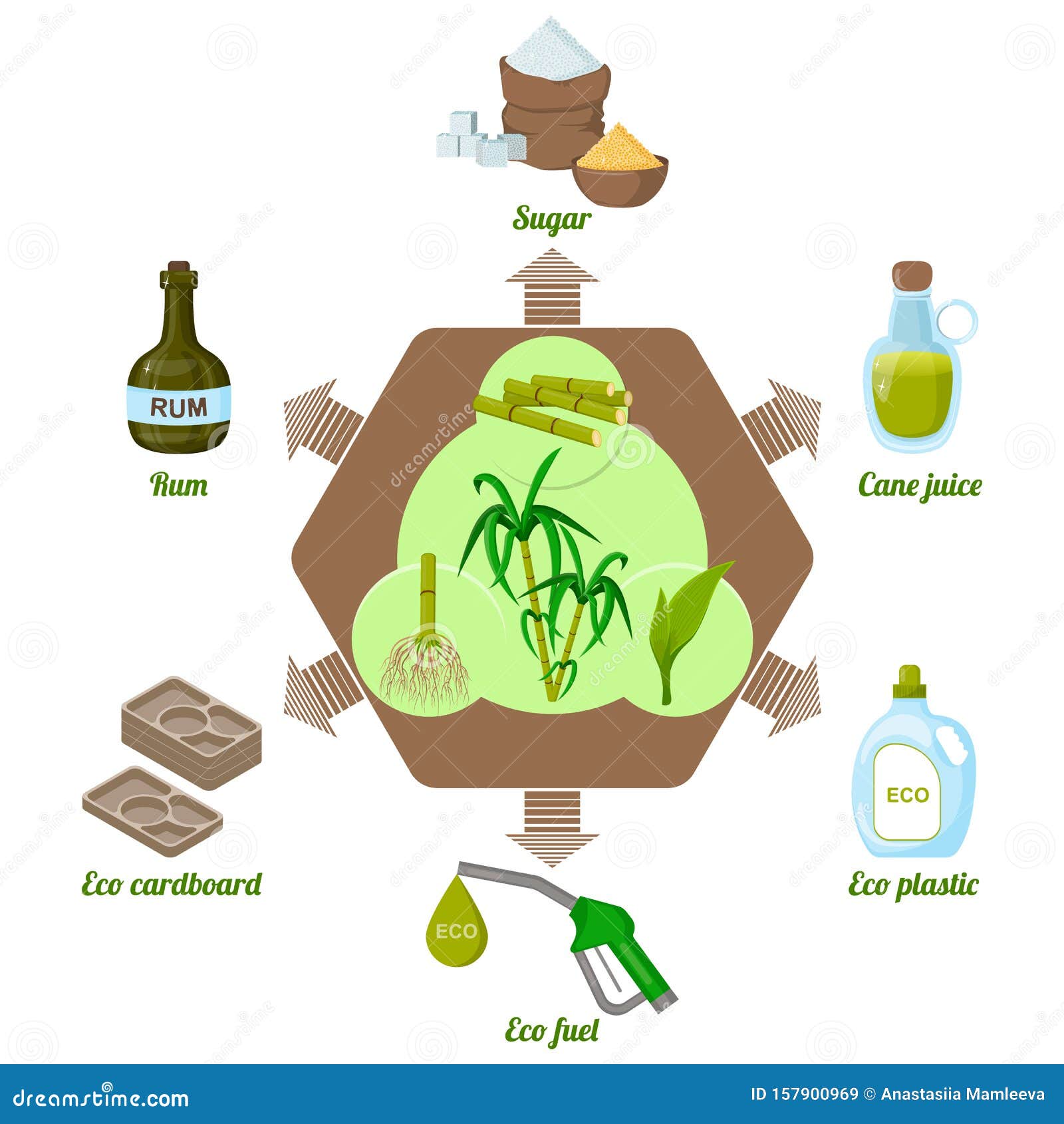
While sugar cane is primarily recognized for its sweet taste, its convenience extends much past plain sweetness. This resilient plant functions as the source for a myriad of items that deal with diverse industries. Ethanol, stemmed from sugar cane fermentation, plays an essential role in sustainable power, working as a cleaner option to nonrenewable fuel sources. In addition, molasses, a byproduct of sugar refining, is used in animal feed, in addition to in cooking and fermentation processes.Sugar cane's coarse deposit, known as bagasse, is not wasted; it is transformed right into biodegradable product packaging materials and offers as a biomass gas resource. Different sugars and syrups gotten from sugar cane find applications in the food and beverage field, adding to flavoring and preservation. The plant's fallen leaves can be utilized for thatching, while its juice is taken in as a rejuvenating beverage in many societies. Subsequently, sugar cane exhibits agricultural potential beyond its sweet track record.
Innovations in Sugar Cane Handling
As improvements in innovation remain to improve different sectors, sugar cane handling is experiencing a considerable transformation. Modern developments, consisting of automated harvesting and accuracy agriculture, are enhancing efficiency and yield. Drones and sensing units keep an eye on crop wellness, allowing farmers to enhance watering and nutrient application, ultimately enhancing productivity.In processing facilities, modern machinery and devices streamline operations. Advancements such as enzymatic processing and progressed filtration techniques enhance the removal of sugar while reducing waste. Furthermore, the adoption of real-time data analytics makes it possible for manufacturers to keep an eye on procedures closely, making sure quality control and lowering downtime.Biotechnology is also playing a critical function; genetic engineerings enhance sugar cane's resistance to insects and environmental stressors. These innovations not only add to higher sugar yields yet also promote the production of diverse byproducts from the cane, expanding its commercial applications. Overall, these advancements are paving the method for a more efficient and lasting sugar cane processing market.
The Future of Sugar Cane: Sustainability and Bioproducts
The future of sugar cane manufacturing is significantly intertwined with sustainability and the advancement of bioproducts. As worldwide need for environmentally friendly options increases, the sugar cane industry is rotating towards methods that decrease ecological impact. Innovations in growing methods, such as accuracy farming and integrated parasite management, aim to improve return while decreasing resource consumption.Furthermore, sugar cane is being explored as a raw material for biofuels, bioplastics, and various other lasting items. These bioproducts not only provide a renewable option to typical visit fossil gas and plastics yet additionally add to a round economic climate by using waste materials.Research and development in biotechnology are leading the way for boosted sugar cane varieties that need less water and plant foods, further promoting sustainability. By embracing these advancements, the sugar cane sector can secure its future while attending to crucial ecological difficulties, demonstrating its potential as a keystone of sustainable development.
Regularly Asked Concerns
What Are the Ecological Influences of Sugar Cane Farming?
The ecological impacts of sugar cane farming consist of logging, soil deterioration, and water air pollution. In addition, Click Here using chemicals can harm biodiversity, while monoculture methods minimize ecosystem resilience, presenting long-lasting sustainability obstacles for agricultural techniques.
Just How Does Sugar Cane Compare to Other Sweeteners Nutritionally?
Sugar cane, rich in carbs, gives power yet lacks necessary nutrients compared to alternatives like honey or maple syrup, which provide nutrients. Its high glycemic index additionally elevates concerns over blood sugar spikes.
What Are the Health Advantages of Consuming Sugar Cane Products?
The health and wellness advantages of consuming sugar cane items include enhanced digestion, enhanced energy degrees, and potential antioxidant buildings. In addition, they might sustain hydration and supply crucial nutrients, adding favorably to general wellness.
How Is Sugar Cane Waste Utilized After Processing?
After handling, sugar cane waste is made use of in numerous means, consisting of biofuel production, animal feed, and natural plant foods. This lasting technique lowers environmental impact while making best use of resource performance within the sugar industry.
What Are the Historical Beginnings of Sugar Cane Growing?
